Note: We are pleased to reprint this paper on the Colombian emerald mines.
The Emerald Deposits of Muzo, Colombia†
By Joseph E. Pogue,* Ph. D., Evanston, Illinois
Transactions of the American Institute of Mining Engineers
Vol. LV, 1917 (Arizona Meeting, September, 1916)
*Assistant Curator, Division of Mineralogy and Petrology, U. S. National Museum.
† Received June 28, 1916
|
The writer visited the Muzo emerald mines in July, 1915, and spent six days in their study. This paper embodies the results of his observations, plus information personally communicated by Robert Scheibe, Professor of Geology in the Mining Academy of Berlin, who at the time of the visit was completing a detailed field investigation of nearly a year’s duration of the emerald deposits of Colombia. An elaborate account of this valuable work may be expected at a future date from the pen of Professor Scheibe.
Location
The Muso emerald deposits are
situated in the western foothills of the eastern branch of the Colombian
Andes and are distant about 96 km.1 (60
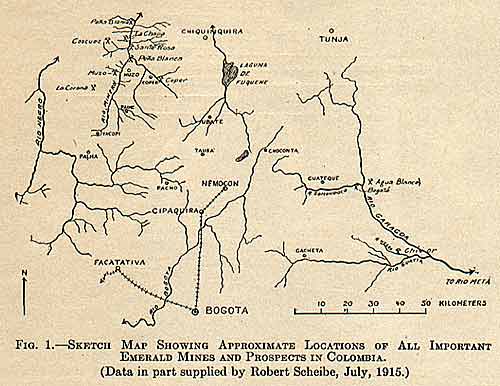
miles ±) in a direct northwesterly line from Bogotá,
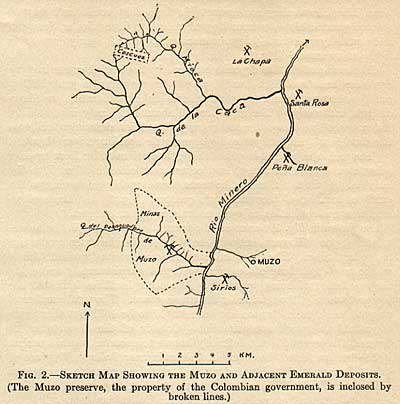
the capital of Colombia (Fig. 1). They lie about 8 km. by trail west
of the small village of Muzo in the Department of Boyaca, and embrace
about eight great open cuts, closely grouped, occupying a portion
of a steepwalled valley, that of the Itoco, also called Quebrada
del Desaguadero, an affluent of Rio Minero which empties into the
northward-flowing Magdalena, the great artery of commerce for central
Colombia. Though distant but 33 km. from La Dorada, the head of steam
navigation on the lower Magdalena, they are inaccessible from
that point, and may be reached practicably only from Bogotá via
rail to Cipaquira or Nemocon and thence by mule for 2 1/2 days over
an execrable trail, nearly impassable in the rainy season2 (Fig.
1).
The
region about the deposits is intensely tropical,
characterized by excessive heat and high humidity,
with a rank jungle growth that quickly obscures
abandoned workings and makes exploration peculiarly
difficult and costly.3 The
region round about is sparsely inhabited by
Indians who live in squalor and poverty — modified
descendants of warlike aborigines, docile and
peaceable, even servile, speaking a Spanish patois.
The
region in general is unhealthful; the natives
suffer from tropical anaemia, malaria,
dysentery, and other complaints incidental
to the latitude. Work in the mines, however,
is reasonably safe owing to the excellent
location of the workmen's quarters (Fig.
3) and the medical attention and sanitation
enjoyed under recent management.
|
As shown in Fig. 1, the emerald occurs at other points in the mountainous region of Boyaca, but only the Muzo locality has been productive in modern times. The so-called Somondoco deposits (marked Chivor on the map) and those of Coscuez are important historically and enjoy the reputation of being very rich. The other localities indicated are prospects merely, though locally known as minas. The total number of emerald localities in Boyaca has been stated to be 157,4 but this figure is probably a rough approximation. Outside of the Department of Boyaca, the emerald is not definitely known to occur in South America. It has been reported, however, in Colombia near Bolivar, Province of Velez, Department of Santander,5 and tradition points to the Manta Valley near Puerto Viejo in Peru as a source,6 but it seems probable that all the “Peruvian” emeralds came from the Colombian deposits.
|
The present section is preliminary to a fuller study under preparation on the history and archeology of the emerald in South America.
The early history of the Muzo deposits is buried in the remote past. These, in common with the Somondoco (Chivor) and Coscuez deposits, had long been worked when the Spaniards first set foot in the New World.7 The three formed the principal, probably the sole, sources of the precious green stone that the Spaniards found so widely distributed through northwest South America and particularly in the realm of the Incas in Peru–a product that shared with gold in the role of inciting the cupidity of the invaders and enticing them to brave the dangers of the unknown interior.
|
Although they soon conquered the Chibcha Indians, the Spaniards met with stubborn resistance from the Muzos, an uncultured and warlike tribe, who like their neighbors, the Chibchas, were in possession of emerald deposits, but were more successful in keeping from their white enemies a knowledge of the localities. They hid all traces of emerald mining for 20 years, though in 1555 Luiz Lanchero founded the village of Muzo in their midst, incited, it seems, by the belief, based on rumor and more pointed information, that the nearby Itoco mountains had yielded the emerald in abundance.13 In 1558 mining operations were begun by the Spaniards in these mountains and for a time actively prosecuted in the face of repeated attacks by the Indians. The locality, however, was subsequently abandoned and the mine became overgrown with jungle, and its position has not since been discovered.14
|
About the year 1594 the Spaniards succeeded in finding the Indian workings nearby at the site of the present-day Muzo mines,15 and then commenced active work and for some 15 years or more the output was considerable.16 The production, however, soon fell away, owing to labor difficulties,17 and toward the middle of the 17th Century the Spanish Crown, whose fifth portion18 had dwindled, reorganized the industry under the direction of the Royal Treasury. Its administration seems to have been singularly inefficient; excessive labor in the mines was imposed on neighboring tribes, a burden resulting in heavy mortality and serious depopulation of the region; dishonesty on the part of both workers and officials19 still further lessened the output; and the galleries that were earlier worked were abandoned for open-cut operations, a change not immediately productive of results. Ineffective mining continued to the middle of the 18th Century or thereabouts, when a disastrous fire terminated activities for a time. Work was later resumed but prosecuted only in a desultory fashion until the success of the War of Independence in 1819 transferred the holdings to the new-born Republic. The republican Government at the outset lacked the organization necessary for running the mines, but realizing their possibilities as a source of revenue, soon contracted for their private exploitation, the terms being 10 per cent. of the net profits.20 The mines were worked under lease from 1824 to 1848,21 when Congress in Bogotá decreed that all emerald deposits found in the country should be worked under the direction of the nation.22 This decree does not seem to have been strictly adhered to, for contracts with private parties were subsequently entered into by the Government, some being in the nature of partnerships, others being strict concessions.
|
It would be scarcely profitable, even if trustworthy data were available, to follow in detail the vicissitudes of the various arrangements made from 1848 to 1909.23 Suffice to say that the Muzo mines were worked almost continuously during that period, but their development suffered from a lack of any sustained policy of administration as well as from the want of engineering and geological advice. In 1909, the Government closed a partnership contract with an English company, The Colombian Emerald Mining Co., Ltd., controlled by South African diamond interests,24 and the deposits were actively exploited for a time; but after a few years the contract was rescinded25and the Government reassumed sole control of the mines. Operations have been totally suspended, however, since Jan. 1, 1913, owing to the fact that the appropriations for administration and exploitation, being entirely insufficient for reestablishing mining activity,26 were applied merely to the maintenance of the property. The European War, in its effect on the precious stone market, precludes profitable exploitation in the immediate future.
General
Geology
The
geology of the
Eastern Cordillera
of the Colombian
Andes is known
only in the most
general way.27 The principal
geological formations
exposed in the
emerald-bearing
region are shown
in the following
columnar statement:28
Quaternary
Tertiary
Cretaceous
- Red sandstone with septarian nodules.
- Compact sandstone; gray fossiliferous limestone between two layers of gray shale with plant impressions.
- Black, carbonaceous shale and shaley limestone. Carries Muzo emerald deposits and Cipaquira salt deposits.
- Siliceous schists and conglomerates, with jasper, flint, etc.
These rocks are compressed into great north-south folds and igneous phenomena are largely lacking.
Detailed
Geology
General.–The
geological relations
of the emerald
deposits are
well exposed
in the great
open cuts made
in exploitation
of the emerald
veins, but the
surrounding conditions
are almost completely
hidden by
dense jungle growth
(Fig. 3). The
emeralds are
found almost
entirely in calcite
veins that traverse
a black, carbonaceous,
rather intensely
folded formation
consisting of
thin-bedded shale
and limestone
(Fig. 4).
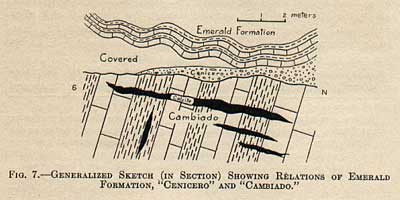
This
emerald formation29 lies
discordantly30 upon
steeply dipping strata, barren of emeralds,
composed of heavier beds of carbonaceous
limestone intercalated with black shale,
and called the Cambiado from the
Spanish word cambiar, to change.
Between the emerald formation and the Cambiado and
ever in close proximity to the plane of
discordance are three rock types of great
significance in furnishing direct evidence
of the origin of the emeralds. These are
(1) albite rock, (2) a light-gray rock
composed of a soft granular aggregate of
calcite, dolomite, quartz, pyrite, and
other minerals, called by the miners Cenicero (Spanish cenicero =
ash) in allusion to its ash-like appearance,
and (3) aggregates of large, well-formed
calcite rhombs in a fine-grained matrix,
forming rock masses known locally as Cama, from
the Spanish word cama, meaning bed.31 In
addition, a few pegmatite veins have recently
been discovered in the deposits.
|
|
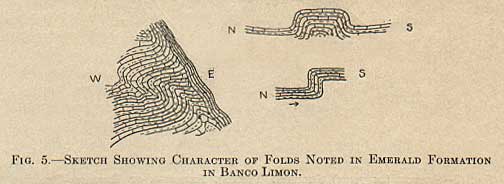
Well-defined joints are inconspicuous; faults are present, but, with the exception of the plane of overthrust separating the emerald formation and the Cambiado, are for the most part not easily traced.
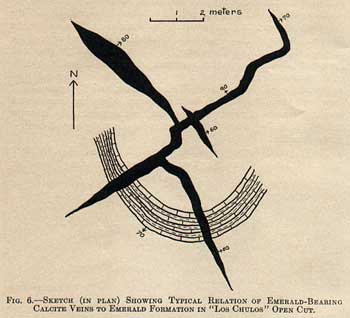
The emerald is seldom found in the shale or limestone alone. Its usual home is the calcite veins. In many places the beds carry nodules of pyrite or seams of that mineral in well-crystallized condition; and some phases are shot through with well-formed pyrite crystals.
The emerald formation rests discordantly upon the Cambiado. The plane of discordance is usually found to be sharp and clear-cut; in many places it is marked by the presence of albite rock, Cama, or Cenicero.
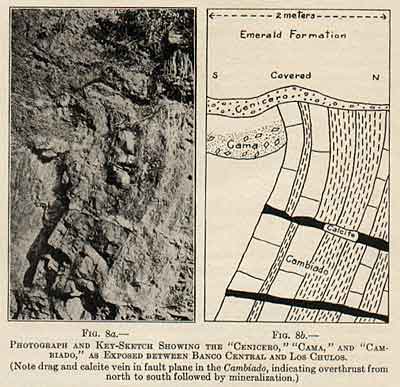
The Cambiado.– (See Figs. 8a and 8b). This formation consists of beds of black, crystalline limestone, averaging in thickness about 25 cm. and alternating with thin-bedded shale similar to that of the overlying emerald formation. The limestone shows itself under the microscope to be composed of ragged, granular masses of calcite, inclosed in black carbonaceous matter, and carrying a few to many fragmental crystals of albite. This rock in places grades upward into a phase in which albite predominates, the so-called albite rock described later; downward it grades presumably into albite-free limestone, but only the topmost few meters of the Cambiado are in any place exposed.
|
The surface of the Cambiado, that is, the plane of discordance, is exceedingly irregular, characterized by sudden changes in inclination, steep slopes, and prominent hollows. Its general shape is that of a huge bowl-like basin with undulating bottom. Its topographic configuration is so complex, its horizontal development so subordinate, that, apart from the fact that the overlying beds are intensely folded while the underlying ones have uniform inclination, it seems evident that the contorted emerald-bearing strata have been shoved bodily into their present position upon the Cambiado. The presence of some brecciated shale and marked mineralization along this plane, as well as evidences of faulting and drag in the upper part of the Cambiado (Figs. 8a and 8b), corroborates the interpretation of overthrust.
|
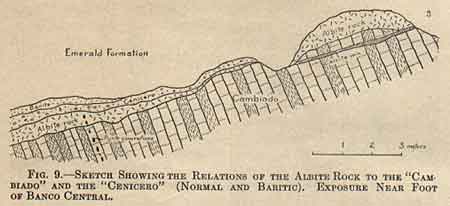
The albite rock clearly represents a phase of the Cambiado limestone that has been metamorphosed by mineralizing solutions (or vapors), part of the calcite having been displaced and albite added.
The relation of the albite rock to the Cambiado and also to the Cenicero is shown in Fig. 9.
|
The Cama.– This
formation is composed of conspicuous rhombs
and rhombic twins of calcite, most of them
from 5 to 10 cm. in diameter, set in calcareous
cement along with some quartz, the whole
forming a breccia-like mass (Fig. 10). The
habit of the calcite, which occurs as
unit rhombohedrons alone or modified by base,
and as twins of the first-named form with
(1010) as the twinning plane, probably reflects
the temperature range of development.34 This
formation rests directly upon the Cambiado, but
is not continuous, being found only here
and there, either alone or close to the somewhat
similarly occurring Cenicero (see
Fig. 10).
The Cama in
places shows plainly a connection
with calcite veins both in the emerald
formation above and in the Cambiado below.
Some calcite veins in the latter
have the peculiar calcite crystallization
of the Cama.
The Cenicero.– This formation occurs as irregular lenses or beds up to a meter or so in thickness present in many places between the emerald formation and the Cambiado, either with or without the Cama (Fig. 10). It is connected below with the albite rock, into which it locally grades, but unlike the Cama, shows no connection with the calcite veins traversing the overlying and underlying formations. In a few places it was noted forming vein-like bodies in the emerald formation itself.
|
The
ordinary Cenicero is a crumbly,
light-gray aggregate of crystals, chiefly
of calcite, dolomite, quartz, and pyrite.
A typical specimen under the microscope
shows the minerals noted as well-formed,
fragmental, and rounded crystals, set in
a fine-grained ground, difficultly resolvable,
but probably mainly calcareous matter,
stained with a little carbonaceous matter.
Toward its top the Cenicero in many
places carries abundant fragments of black
shale a centimeter long and smaller, forming
masses of breccia rarely seen over 2 m.
in thickness.
There
are three more or less strongly marked
phases of the Cenicero– dolomitic,
pyritic, and baritic–the normal sequence
upward being in that order (Fig. 9).
In addition, the lowermost part in many
places is albitized, while the topmost
portion is nearly everywhere connected
with the emerald formation by the breccia
phase just noted. The baritic phase is
locally seen as an almost pure layer of
massive to nodular barite, with a maximum
thickness of about 40 cm.
Pegmatites.– Pegmatite dikes were discovered in 1915 by Robert Scheibe in the Cambiado near Banco Amarillo and in a ravine back of Banco Central. The last-named locality was visited35 and the pegmatite, here about 2 m. in width, found to consist of quartz, in part well crystallized (the low-temperature form), and decomposed feldspar, together with a few crystals of albite and apatite, much greenish to clear allophanite, many small form-rich crystals of pyrite, and a little hyalite.
Minerals
The Muzo deposits present a notable assemblage
of minerals, many of them well developed crystallographically
and some of particular chemical interest.
The present section assembles the geologically
significant characteristics of these minerals,
but attempts no detailed mineralogical
description. A good crystallographic study
was published in 1904 by H. Hubert36 and
an accurate mineral list with brief characterizations
in 1915 by Lleras Codazzi.37 The
statements here given are the results of
the writer's observations, except where otherwise
noted.
Emerald.– Usually
found in pockets, or embedded, in calcite
veins traversing the emerald formation; rarely
embedded in that formation itself or in the Cenicero. Closely
associated minerals forming the emerald gangue
are: Calcite, dolomite, parisite, pyrite,
quartz, barite, fluorite, and apatite,
the last three very rare. The emerald occurs
as six-sided prisms with base, some with
rarer forms also. Few crystals are larger
than the thumb. Most crystals are clear when
first taken from the matrix, but later develop
cracks; some fall to pieces upon removal.38
Choice
specimens show a rich green color surpassed
by the product of no other locality.
Some crystals display zones of color;
a few are dark to black with inclusions
of carbonaceous matter. In some specimens
recently found, the carbonaceous matter
is arranged in a six-rayed
figure centering about a tapering hexagonal
core. One such specimen was examined
optically in basal section and proved
to be of the same orientation throughout;
it therefore does not represent a twinned
crystal as suggested by Lleras Codazzi.39 Its
re-entrant angles are presumably the
effect of solution and the disposition
of the carbonaceous inclusions, the expression
of crystallizing forces, as shown also,
for example, in chiastolite.
|
Calcite.– Forms emerald-bearing veins in the emerald formation and barren veins in the Cambiado, and is well crystallized where occurring in vugs. Crystals are water-clear to opaque from disseminated carbon; they show a rich variety of forms, with two dominant habits, rhombohedral and prismatic. Closely associated with emerald, pyrite, and parisite. Occurs in the Cama as conspicuous unit rhombohedrons (some modified by base) and as rhombic twins, twinning-plane (1010). Is an important component of the Cenicero as small rhombs and grains.
Dolomite.– Occurs as small, transparent, honey-yellow rhombs in the emerald veins and in the Cenicero.
Ankerite.– Occurs as yellowish or brownish rhombs in the emerald gangue; one variety has been reported as carrying a little CeCO3.40
Pyrite.– Occurs in well-formed crystals in the emerald veins; as seams, disseminated crystals, and concretions in the emerald formation; as crystals in the Cenicero; and as crystals and concretions in the Cambiado. The crystals, which range in diameter from a fraction of a millimeter to several centimeters, show a profusion of crystal forms and present three habits, cubic, octohedral, and pyritohedral.
|
Parisite.– This rare mineral, of the composition (CaF)(CeF)Ce (CO3)3,41 was first discovered in the Muzo mines by J.J. Paris, a lessee of the deposits, and named in his honor by Bunsen,42 who investigated the mineral. It occurs as crystalline masses and crystals in immediate association with the emerald. The crystals are double hexagonal pyramids, with or without the base, and most are under 1 cm. in length.
Quartz.– Occurs as well-formed colorless to greenish (rare) crystals in the emerald veins; inclusions of parisite, pyrite, and emerald have been noted.43 Less perfect crystals are found intergrown with calcite rhombs of the Cama. Crystals rich in forms occur in the pegmatite vein back of Banco Central; these are low-temperature quartz, formed below 575°.44
Fluorite.45 – Occurs as small, colorless to greenish crystals in some of the emerald veins; very rare; forms are cubes or cubes modified by small octahedrons; inclusions of emerald noted.46 Has also been noted by Scheibe (oral communication) in the albite rock at one spot.
Apatite.– A few, well-formed, glassy crystals have been found by Scheibe in the emerald gangue and in the pegmatite vein back of Banco Central.
Gypsum.– Present in the emerald formation as well-formed, clear, slender crystals. Presumably a weathering mineral, but Lleras Codazzi47 noted inclusions of parisite, and Olden48 mentioned green gypsum as an associate of the emerald.
|
Barite.– Occurs in conspicuous layers, up to 40 cm. or so in thickness, forming in places the uppermost part of the Cenicero; this phase is nodular to massive.50 Found also as small, glassy, tabular crystals, 2 mm. across, associated with crystallized calcite in some veins in the emerald formation. A small crystal perched on an emerald crystal has been noted by Scheibe.
Anthracite.– Small fragments of impure anthracitic to graphitic carbon are found in joints in the emerald formation.51
Marcasite.– Noted by Lleras Codazzi52 in the form of nodules.
Chalcopyrite.– A few imperfect crystals, stained with a little malachite and azurite, have been found in the workings. Also occurs sparingly in the Cenicero.
Native Sulphur.– Found in conspicuous masses in parts of the Cenicero.
Pyrophyllite.– Occurs as apple-green folia, occupying small, inconspicuous seams in the emerald formation; found either alone or associated with dolomite, pyrite, and quartz.
Allophanite.– Found only locally developed in clay-like masses forming lenses in the emerald formation. Noted by Lleras Codazzis53 in blue masses in a vein in the Cambiado.
Fuchsite.– Noted by Lleras Codazzis54 as green laminae adhering in places to the surface of the shale of the emerald formation.
|
Age
The ages of
the emerald formation and Cambiado are
fixed as Cretaceous by the fossils, chiefly
ammonites, that
have been found rather abundantly in them.
Miguel Gutiérrez55 places
the Cambiado as lower Cretaceous56 and
the emerald formation as middle Cretaceous.57 The
present writer presents no fossil evidence
but feels that further paleontological study
is needed before a correlation closer than “lower
Cretaceous” can be accepted for the
rocks of the emerald deposits. An ammonite
collected by the writer from the stream bed
below the workings has been identified by
Dr. T.W. Stanton as Pulchellia zaleatoides, Karsten,
from the upper part of the lower Cretaceous.
Origin
The evidence
bearing on the origin of the emerald has
been presented in descriptive form. It may
be summarized under four heads, as follows:
1. The association of such minerals as emerald, parisite, fluorite, apatite, albite, and barite in a sedimentary formation implies the introduction of material from an external source. This is so obvious from the composition of these minerals and their known occurrence elsewhere as to render further elaboration unnecessary.
2. The presence of pegmatites is significant, because the conditions under which pegmatites form are fairly definitely understood. The mineral content of the pegmatites is thought to correlate their formation with the general period of mineralization.
3. The presence of albite rock (highly albitized limestone) and its spatial relation to a zone occupied by the Cenicero and Cama indicate the passage of strongly effective mineralizing solutions. The albite rock itself is thought to represent a contact rock, not of the normal type (because of the absence of such characteristic minerals as garnet, epidote, pyroxene, amphibole, etc.) but of the type characterized by V.M. Goldschmidt58 as that due to “pneumatolitic contact metamorphism,” a type that develops later in the cooling of, and more distant from, the parent magma than the normal type.
4. Structural conditions indicate that the emerald formation was overthrust to its present position upon the Cambiado, and that this movement was followed by a period of mineralization which attained its most conspicuous results along the fault plane and its economic results above (and not below) that plane. That the emerald veins are the result of the same period of mineralization that produced the Cenicero, Cama, and albite rock, is thought to be clearly indicated by the mineral content and spatial connection that may be traced between the four. The barren calcite veins in the Cambiado are probably of the same period of mineralization also; for they are post-faulting (Figs. 8a and 8b) and in places are connected with the Cama.
|
Other inferences may be drawn and suggestions made. It is possible that the overthrusting and folding of the emerald formation is due to the crowding effect of the igneous intrusion; this makes an attractive and reasonable hypothesis. Then, the fact that the veins of the emerald formation carry emeralds, while those of the Cambiado are barren, or, in short, that the emeralds all lie above the plane of overthrust, although non-economic mineralization proceeded below, suggests that the solutions, entering along the shattered fault plane, effected a separation there, their liquid portion permeating the rocks on either side, their gaseous portions rising and therefore recording passage (by emerald deposition) only in the rocks above. The presence of the two unusual types of deposits, the Cenicero and Cama, raises a difficult question; but it seems probable that the Cenicero was first deposited, following close on to the faulting movement, and then the Cama was introduced and, accompanying it (farther out from the fault plane), the calcite veins were developed. Again the carbon content of the emerald formation interposes itself as a common factor, suggesting the possibility that it may have been essential to the formation of the emerald in some way, either by its precipitative action, or by its reducing action on chromium, the coloring agent of emerald. Finally, the question arises as to the source of the calcite so prominent in the seams and the veins throughout, and it appears probable that the calcium carbonate displaced from the Cambiado upon its albitization is sufficient to form these bodies, without magmatic contribution of that material.
|
Mining Methods59
The emerald is won exclusively
by open-cut mining. The steep slopes
of the emerald formation, stripped of
their covering of jungle, are worked
in great terraced banks (bancos), affording
benches60 on
which lines of peons stand and attack
the bench below with long iron crowbars
(Figs. 11 and 12). The comparatively
soft limestone and shale are easily broken
away in this way without recourse to
blasting (which would shatter the fragile
emerald crystals) and the emerald-bearing
calcite veins are carefully removed by
hand and taken to a sorting shed above.
The debris falls down the step-like slope
and the accumulation at intervals is
swept down to the creek below by water
led from reservoirs in the mountains
above the workings (Fig. 13).
In
the sorting shed, the calcite veins are
carefully broken by hand and the emerald
crystals picked out. The finer material,
together with gem-bearing debris gathered
from “bed-rock” and from the
water channels below the banks, is washed
on sloping tables and the emerald fragments
withdrawn by boys (Fig. 14). The stones
are separated into a number of grades
according to color, size, transparency,
and freedom from flaws. The product goes
by mule to Bogotá from time to
time, and there awaits transportation
to London in larger consignments.
The
labor is done by Indian peons drawn
from the neighborhood. Mining officials
and police are supplied from Bogotá or
other towns. Great vigilance is exercised,
when the mines are in operation, to reduce
loss by theft. A body of military police
is assigned to the mines; the exits are
carefully guarded; watchmen are always
on duty in small guardhouses on prominent
points above the workings; overseers
are in constant attendance during hours
of work; and the workmen are impounded
and not allowed to leave the mines until
the culmination of a suitable period
of search.
The
mine buildings are commodious and comfortable,
maintained in good condition (Fig. 3).
The mining equipment is simple, but the
fragility of the emerald precludes the
use of most types of equipment that would
increase the quantity of ground handled.
Production
It is impossible
to present an approximation of the total
production of the Muzo mines. The pre-Spanish
output, undoubtedly significant, is of course
not open to any measure. In historic times,
the exploitation was so irregular and the
records so incomplete, that a fair basis
for judgment is entirely lacking. Nevertheless,
it is certain that the total output may be
estimated in terms of tens of millions of
dollars, and that in many single years the
production has run in value from $1,000,000
to perhaps $2,000,000, or more.
|
Other
Deposits
The
Coscuez and Somondoco emerald deposits
have already been mentioned as the
only other important known occurrences
of this mineral in South America.
Coscuez Deposits.– These lie about 12 km. in direct, line north-northwest of the Muzo mines (Fig. 2) but are exceedingly difficult of access. They were known before the Conquest and won a reputation for richness (see p. 914). No information is yet available concerning their geology, but the writer has been informed that a geological study of them was made late in 1915 by Robert Scheibe.61
Somondoco
Deposits.– These lie
about 130 km. in direct line southwest
of the Muzo mines on the Orinoco watershed
(Fig. 1), and a careful
survey of available information suggests
that possibly they are richer than the
Muzo deposits. They have been visited
and described by W. Lidstone62 and
by E. B. Latham;63 and
in 1915 a detailed geological survey
of them was made by Robert Scheibe, but
the results are not yet published.
These
deposits have a romantic history. They
were richly productive before the Spanish
Conquest, were seized and worked a
while by the Spaniards, were subsequently
abandoned and lost, and only rediscovered
in 1896.64 They
have not been productive in recent
times, though foreign capital has interested
itself in their exploitation.
According
to Latham65 the
emerald here occurs in veins of “semi-decomposed
quartz” traversing folded
beds of dark gray to black “clay-slate” and
limestone, and is found either directly
embedded, or in pockets, in these veins,
very rarely in the rock itself. Lidstone66 describes
the occurrence here in a similar manner,
without, however, specifying the vein matter
to be quartz.
Acknowledgements
For
courtesies and valuable help, both during
the writer's visit to the Muzo mines, and
later during the preparation of this paper,
the writer extends his appreciative acknowledgment
to the following: Hon. Marco Fidel Suárez,
Minister of Foreign Affairs, Bogotá;
Hon. Daniel J. Reyes, Minister of Hacienda,
Bogotà; Hon. Thaddeus A. Thompson,
American Minister, Bogotá; Dr. Juan
de Dios Vasquez, Director of the Muzo mines;
Dr. Alfredo Angueyra, Acting-Director of
the Muzo mines at the time of the writer's
visit; Prof. Dr. Robert Scheibe, Professor
of Geology, Royal Mining Academy, Berlin;
Dr. Ricardo Lleras Codazzi, Professor of
Mineralogy and Geology, National University,
Bogotá; Dr. Lucas Caballero, Bogotá;
Dr. Hermano Apolinar Maria, Bogotá;
Phanor James Eder, New York; Douglas B. Sterrett,
U. S. Geological Survey, Washington; Dr.
George P. Merrill, and Dr. Edgar T. Wherry,
U. S. National Museum, Washington; Dr. Ronald
S. Crane, Evanston, and Mrs. Leonard G. Shepard,
Evanston.
Selected Bibliography
- Dimas Atuesta: Informe relativo al levantamiento de los planos y mensura de los Terrenos de las Minas de Esmeraldas de Propriedad de la Nacion, manuscript, 1898. (Consulted at Muzo Mines. English translation on file, U. S. Geological Survey, Washington.) Description, chiefly historical and geographical, of the Muzo and Coscuez deposits. Inaccurate.
- Max Bauer: Precious stones, English translation by L. J. Spencer, pp. 312 to 315. London, 1904. Carefully compiled geological, mineralogical, and historical account of the Muzo deposits.
- Miguel Gutiérrez: Estudio Geologico de las Minas de Esmeraldas de Muzo, Anales de Ingeniería, pp. 3 to 14 Bogotá (1913). Gives results of field study of Muzo deposits. Observations incomplete; interpretations open to question.
- H. Hubert: Sur les Minéraux associes a l’Emeraude dans le Gisement de Muso (Nouvelle-Grenade), Bulletin Musee d’Histoire Naturelle, vol. 10, pp. 202 to 208, Paris (1904). Detailed crystallographic study of emerald and associated minerals from Muzo.
- Ricardo Lleras Codazzi: Los minerales de Muzo, Contribución al estudio de los minerales de Colombia, Imprenta de la Cruzada, pp. 3 to 7, Bogotá (1915). Good, brief description of the Muzo minerals.
- Charles Olden: Emeralds: Their Mode of Occurrence and Methods of Mining and Extraction in Colombia, Transactions of the Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, vol. 21, pp. 193 to 209 (1911). Good account of mining methods at Muzo. Includes geological description and historical details, the latter in part unreliable.
- A. Stülbel and W. Reiss: Geologische Studien in der Republik Colombia, Reisen in Süd-Amerika, vol. 2, pp. 43 to 48, Berlin (1899). Geological and mineralogical description of the Muzo deposits.
- H. A. Schumacher: Ueber die columbischen Smaragden, Zeitschrift der Gesellschaft für Erdkunde zu Berlin, vol. 10, pp. 38 to 62 (1875). A detailed and valuable historical description of the Muzo mines, based on original sources.
Discussion
EDGAR T.
WHERBY, * Washington,
D. C. (communication to the Secretary†)
.–Dr. Pogue’s presentation of the
facts concerning the emerald deposits is
very clear and convincing, and the only addition
that I can suggest is a summary of previous
theories of origin. He makes it evident that
the pegmatite theory is the only one capable
of explaining the existing relations, but
upon certain details there may be some difference
of opinion. If I understand the term pneumatolytic,
it does not imply that all the elements concerned
in a given deposit were transported as gases,
but rather that the crystallization of these
elements into the various minerals was favored
by the presence of certain gaseous substances,
notably H20, CO2 and
HF. It is highly improbable that the oxides
of glucinum, aluminum, chromium, and silicon,
which enter into the composition of the mineral
emerald could have been transported in the
gaseous form. The same is true of the metallic
constituents of the parisite and other associated
minerals. The explanation suggested, that
solutions separated into liquid and gaseous
portions, the latter ascending and forming
the emerald in the upper portions of the
rock only, therefore, seems to me untenable.
When two formations exist side by side and one, A, is mineralized while the other, B, is barren, the possible explanations may be classed as (1) chemical, and (2) physical.
1. Some chemical feature of A not found in B might have caused crystallization of certain minerals in the former, which did not appear in the latter. In the present instance both rocks appear to be so similar chemically that no such effect can be looked for. Pogue mentions carbon as a possible precipitating agent, but describes both formations as carbonaceous, so that the difference in the minerals of the two can not be thus explained.
2. The physical condition of A might have permitted or encouraged the passage of the solutions, while that of B retarded or prevented it. In the present deposit some mineralization occurs in both formations, calcite veins, albite, and pyrite being found in both, whereas emerald, parisite, and a number of minerals of minor importance occur only in the upper, A. It seems to me that this difference may have been produced by a change in the composition of the solutions during the progress of mineralization; at first these brought in only the constituents of albite and pyrite and deposited them with calcite dissolved from the wall rock, in both formations; the openings in B became completely filled, while the more numerous or larger ones which would naturally have developed in A, since it was the uppermost formation, remained partially open. Then, when during later phases of the mineralizing activity the constituents of emerald and parisite appeared, they were deposited only in A because B had become impermeable.
* Associate Professor of Geology and Mineralogy, Northwestern University.
- This figure was obtained by scaling off the distance on a map of central Colombia, scale 1/810,000, by William Lidstone, C.E., published by Edward Stanford, London, June, 1899, probably the most reliable map of that region; and checked on the Mapa de la Republica de Colombia by Enrique Vidal, Bogotá, 1914, scale 1/2,700,000, the best general map of the Republic. Colombian maps, however, are far from accurate in the modern sense, and on many the Muzo mines (or the nearby village of Muzo) are inaccurately located. In the literature, too, their location is generally erroneously stated, even Bauer (Precious Stones, English translation by L.J. Spencer, p. 314, London, 1904) placing them 150 km. from Bogotá, though possibly this figure is intended to represent the distance by trail, a fair estimate in that event.(back to text)
- There are two direct routes to the mines: (1) Nemocon to Ubaté to Coper to Muzo; and (2) Cipaquira to Pacho to San Cayetana to Paime to the mines. The first is the better; the mine traffic goes by this route. Outfitting is less inconvenient at Cipaquira than at Nemocon.(back to text)
- The mines lie about 800 m. above sea level.(back to text)
- V. Levine: Colombia, p. 116, New York, 1914. (back to text)
- Levine: Ibid., p. 152. This locality is probably authentic, for it is only about 60 km. northeast of Muzo, in the line of strike of the emerald-bearing formation. (back to text)
- Joseph de Acosta: The
Natural and Moral History of the Indies, reprinted
from English translation by E. Grimston,
1604; edited by C. R. Markham, p. 225,
London, 1880. (back
to text)
Jorge Juan and Antonio de Ulloa: A Voyage to South America, translated from the Spanish, 3d ed., vol. 1, book 6, Chap. 9, p. 466, London, 1772. - Vicente Restrepo (Los Chibchas antes de la conquista española, vol. 1, p. 125, Bogotá, 1895) as a result of his archeological study of the Chibcha Indians who inhabited the plateau region east of the Muzo deposits, says: “The Chibchas valued emeralds highly, and as the mines of Muzo which produced the finest of these stones were in the hands of their enemies, the Muzo Indians, they exploited the deposits of Somondoco, which were very rich before the Conquest.” (back to text)
- H. A. Schumacher: Ueber die columbischen Smaragden, Zeitschrift der Gesellschaft für Erdkunde zu Berlin, vol.10, p. 42 (1875). (back to text)
- Detailed, but slightly variant, accounts of the expedition to the mines may be found in Fray Pedro Simon: Noticias Historiales de las Conquistas de Tierra Firme en las Indias Occidentales, Bogotá, 1891; and in L. Fernandez de Piedrahita: Historia General de la Conquista del Nuevo Reyno de Granada, Antwerp, 1688; Bogotá, 1881. (back to text)
- Some confusion of terms has arisen. These deposits are near the valley of Chivor, and have been called the Chivor deposits. Under Spanish dominion they came to be known as the Somondoco deposits, from the fact that the emeralds mined were sorted in the village of Somondoco; and by this name they are generally called in the literature. They do not, however, occur on Rio Somondoco, but other less important deposits are known on that stream. (back to text)
- Although the statement to follow needs substantiation by further archeological research, the Somondoco deposits seem to have been the most important source of the emerald in pre-Spanish time, overshadowing in output the Muzo mines. (back to text)
- Schumacher: op. cit., p. 42. Later the Conquerors turned their attention anew to these deposits and carried on extensive mining operations, if we may judge from the reports of W. Lidstone: Emerald Mines of Chivor, Colombia, Bogotá, 1906, manuscript, copy on file, U.S. Geological Survey, and E.B. Latham: The Newly Discovered Emerald Mines of “Somondoco,” School of Mines Quarterly, Columbia University, vol. 32, pp. 210 to 214 (1910–11), who describe extensive tunnels, ditches, and other excavations found at the locality. Lidstone indeed cites the account of a Spaniard (Alonzo Solis de Valenzuela; no reference) as authority for the statement that 1,200 men were employed in the mines, even in 1565. The Somondoco deposits were lost following the War of Independence and were only recently rediscovered. (back to text)
- Schumacher: op. cit., p. 43. (back to text)
- The statements above
are based principally upon Schumacher,
who seems to have made a fairly thorough
search into a number of original sources
not yet available to the present writer.
Acosta (Compendio histórico del
descubrimiento y colonización de
la Nueva Granada, Paris, 1848; Bogotá,
1901, English translation in manuscript
by Isabel Sharpe Shepard, Chap. 18) gives
a somewhat different version: He writes
that a few years after the founding of
Muzo, the Spaniards discovered the present
Muzo deposits and began mining operations
there in 1568; a rich vein was found prior
to that date at Abipí, 2 1/2
leagues distant, but was not worked, for
lack of water, and its whereabouts became
lost.
Charles Olden (Emeralds: Their Mode of Occurrence and Methods of Mining and Extraction in Colombia, Transactions of the Institution of Mining and Metallurgy (1911), vol. 21, p.194) writes that at the outset operations were confined to the Coscuez deposits, but the present writer has thus far been unable to find any historical basis for this statement. The Coscuez deposits, according to Dimas Atuesta (Informe relativo levantamiento de los planos y mensura de los Terrenos de las Minas de Esmeraldas de Propriedad de la Nacion, manuscript, 1898, English translation on file, U.S. Geological Survey) were discovered by the Spaniards after the Muzo mines were under operation; they were then worked for a period, abandoned, reworked preceding the War of Independence, abandoned, and recently rediscovered. (back to text) - According to Atuesta (op. cit.), Captain Juan Penagos was the discoverer. (back to text)
- By 1612, according to Simon (cited by Acosta, op. cit., Chap. 18), emeralds to the value of 300,000 pesos had been deposited in the royal coffers as the fifth portion accruing to the Spanish Crown. (back to text)
- Fresle (Conguista y descubrimiento del Nuevo Reino de Granada, p. 228, Bogotá, 1859), writing of conditions in the year 1636. (back to text)
- According to a royal edict of 1504, a fifth portion of the mining products of the Spanish colonies went to the Crown. (back to text)
- Schumacher: op. cit., p. 45. (back to text)
- Schumacher: op. cit., p. 48. (back to text)
- One of the first lessees was J.J. Paris, the close friend of the powerful Bolivar. In 1828, Paris obtained the concession for himself alone, which he maintained until 1848. (back to text)
- Schumacher: op. cit., p. 49. (back to text)
- M. Ancizar (Peregrinacion de Alpha por las Provincias del Norte de la Nueva Granada, en 1850, I 51, p. 50, Bogotá, 1853) visited the Muzo mines in 1850 and found them under “active and intelligent exploitation.” This could not be said of many regimes, until very recent years. (back to text)
- P.J. Eder: Colombia, p. 160, London (1913). (back to text)
- As a result, suit was brought in the English courts and judgment was rendered according to which a settlement was reached upon the payment of a consideration on the part of the Government to the emerald company. See Message of the President of Colombia to the Congress of 1914, July 20. (back to text)
- Message of the President of Colombia to the Congress of 1914, July 20. (back to text)
- No detailed studies have thus far been published. The best general accounts are those by A. Hettner (Die Kordillere von Bogotá, Petermann’s Mitteilungen, Erganzungsheft 104, 1891) which includes a generalized geologic map; and Hans Stille: Geologische Studien im Gebiete des Rio Magdalena, with geologic cross-section, Stuttgart, 1907. (back to text)
- In part from personal communication of Dr. Ricardo Lleras Codazzi. (back to text)
- Known locally as capas esmeraldiferas. (back to text)
- This term is used in lieu of “unconformably,” because the latter implies an erosion interval; the “plane of discordance” under consideration is interpreted as due to overthrust and it is not definitely known whether younger beds were thrust over on to older, or older on to younger, or part of a formation on to another part of itself. (back to text)
- It seems advisable to retain the Spanish terms in the following descriptions. (back to text)
- Much of the emerald formation might be called with equal propriety either calcareous shale or argillaceous limestone. The silicate material present is shown by the microscope to be, in part, finely comminuted, unweathered, colorless, mineral fragments, probably quartz and feldspar. Possibly some of this was introduced by the mineralizing solutions. (back to text)
- By Scheibe. (back to text)
- Crystal habit is often controlled by external conditions attending crystallization and therefore will become significant when we possess criteria for interpreting it. (back to text)
- Under the guidance of Prof. Scheibe. (back to text)
- H. Hubert: Sur les Minéraux, associés à l’Emeraude dans le Gisement de Muso (Nouvelle-Grenade), Bulletin Musée d’Histoire Naturelle, vol. 10, pp. 202 to 208, Paris. (back to text)
- Ricardo Llerae Codazzi: Los minerales de Muzo, Contribución al Estudio de los Minerales de Colombia, Imprenta de la Cruzada, pp. 3 to 7, Bogotá (1915). (back to text)
- Max Bauer: Precious Stones, Spencer’s translation, p. 315, 1904. (back to text)
- Op. cit., pp. 6 to 7. (back to text)
- Lleras Codazzi: op. cit., p. 5. (back to text)
- E.S. Dana: System of Mineralogy, p. 290. (back to text)
- Annale der Chemie und Pharmacie, vol. 53, pp. 147 to 156, 1845. (back to text)
- Lleras Codazzi: op. cit., p. 6. (back to text)
- Determined by the method of Wright and Lareen, American Journal of Science, vol. 28, p. 423, 1909. (back to text)
- Noted by Scheib oral communication; by Llerae Codazzi, op. cit., p. 5; by W. Reiss and A. Stubel: ,Geologische Studien in der Republik Colombia, Reisen in Süd-Amerika, Berlin, vol. 2, p. 47,1899; and by Hubert, op. cit., p. 202. (back to text)
- Lleras Codazzi: loc. cit. (back to text)
- Op. cit., p. 5. (back to text)
- Op. cit., p. 196. (back to text)
- Six forms were noted by Hubert, op. cit., p. 203. (back to text)
- It is notable that such a conspicuous mineral remained undiscovered until the visit of Scheibe in 1915. (back to text)
- A specimen was given the writer by Dr. Lleras Codazzi. (back to text)
- Op. Cit., p. 5. (back to text)
- Op. Cit., p. 5. (back to text)
- Op. Cit., p. 5. (back to text)
- Miguel Gutierrez: Estudio Geológico de las Minas de Esmeraldas de Muzo, Anales de Ingeniería, pp. 5 to 8, Bogotá, 1913. (back to text)
- On the basis of Crioceras Roemeri Ammonites compressissimus, D’Orb. (back to text)
- On the basis of Hoplites auritus, Sow. H. Deshayesi, Leym. H. tardefurcatust? Leym. Schloembachia cristata, Defr. sp. Inoceramus Cuvieri, Sow. (back to text)
- Leith and Mead: Metamorphic Geology, pp. 143 to 144, 1915. (back to text)
- This subject is treated in some detail by Olden: Emeralds: Their Mode of Occurrence and Methods of Mining and Extraction in Colombia, Transactions of the Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, vol. 21, pp. 193 to 209, 1911. The mines were not in operation at the time of the writer’s visit. (back to text)
- The benches are about 76 cm. high and 76 cm. broad. Vol. LV.–59. (back to text)
- Personal communication from Dr. Juan de Dios Vasquez, Director of the Muzo mines. (back to text)
- Emerald Mines of Chivor, Colombia, manuscript, Bogotá, 1906, copy on file, U.S. Geological Survey, Washington. (back to text)
- The Newly Discovered Emerald Mines of “Somondoco,” School of Mines Quarterly, Columbia Univ., vol. 32, pp. 210 to 214, 1910–11. (back to text)
- Latham: op. cit., p. 211. (back to text)
- Op. Cit., p. 212.
- Op. Cit.